We used to believe that osteoarthritis (OA) was the result of a lifetime of wear and tear. A disease of old age. We now know that what causes OA to start is wear and tear (Mechanical) but it only progresses in those with poor healing (Systemic). The most common cause of osteoarthritis progression is vascular disease, but it is not the only cause. Understanding how to diagnose osteoarthritis more specifically will improve the treatment of osteoarthritis. This will also help us to understand why stem cell treatment for osteoarthritis is so effective for some and not for others. Who will benefit from from stem cell treatment for osteoarthritis and why will other conditions improve at the same treatment?
Mechanical causes of OA
The mechanical factors that cause the early damage of OA are very common.
- Accidents at work, in the home, in motor vehicles or other locations.
- Elevated Body Mass Index,
- Regular sport,
- Occupation , Regular knee bending and lifting, heavy physical labor, etc. Some jobs have more risk for particular joints. Farmers are more at risk for hip OA,(F) etc.
- Everyday wear and tear
How common is Osteoarthritis
87% of females aged between 55 and 65 have x-ray changes of OA.(L) Over 70 yrs of age they are almost universal. For most people these changes are a fact of life. Most of us do not know that the changes are there until we get an x-ray for some other reason. They are so common, so ‘normal’ that many radiologists do not mention them when reporting the results of the x-rays. For most of the population there are no symptoms, no signs.
Diagnosis – how to diagnose osteoarthritis
Everyone will have wear and tear that can be seen on x-ray. The diagnosis of OA is only made with the presence of pain in the joint. X-ray changes, no matter how severe, is not clinical OA unless you have pain or loss of function.
We may have stiffness, aches and pains that come and go but mostly we manage this with exercises, stretchs, heat, massage and a glass of wine at the end of the day. Yes it is worse when we are tired, stressed or have been more active than usual but we expect this and act accordingly. If we can localize the pain to a joint this may qualify as clinical OA.
However, studies have shown that joint pain and disability in the elderly are equally related to loneliness and depression as they are to severity of joint damage (5) So social support can be a good treatment for OA.
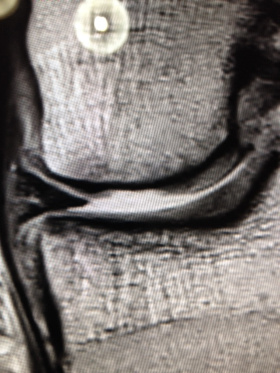
When we started to study osteoarthritis we looked at the x-ray changes in the bone (Osteo) and this gave us a narrow focus for what causes Osteoarthritis. The invention of CT scanners, MRI scanners and lots more tools allowed us to ‘see’ the damage to the cartilage and this then became the focus of research for many years. However, it is now clear that OA has damage in every tissue(6) of the synovial joint; synovium, bone, arteries veins, nerves, muscles (10), ligaments and tendons, not just the cartilage. Cartilage damage may be a red herring. The end product of loss of nutrition from the supporting bone and synovial fluid.
Inflammation is the common pathway.
All of these tissues have stem cells in their Stromal Vascular Fraction that are busy repairing the daily damage that is part of life. Inflammation is the pathway for healing all of these tissues. When damage occurs the body sends out distress signals and stem cells respond by producing inflammatory cytokines. These inflammatory cytokines attract other cells and the healing of acute inflammation begins. When the tissues are healed anti-inflammatory cytokines are released and the inflammation ends.
Chronic inflammation is the problem
Acute inflammation heals and is good. If healing cannot be completed the inflammation can persist. Around three months the bodies reaction changes as the inflammation becomes chronic. Extra blood vessels grow into the area in an effort to improve blood flow for healing. New blood vessels are tender and often cause pain. Connective tissue forms which can impede movement and increase stiffness. Healthy cells and tissues may not be able to recover and as they die stem cells will replace them. However if this continues and the stem cells are forced to work in a hostile environment the performance of the stem cells decreases. Stem cells normally replace themselves and are thus said to be immortal. But, chronic inflammation reduces the flow of nutrients into the area and the removal of toxins slows. Chronic inflammation can kill stem cells.
Stem cell death
As stems cells die and numbers are depleted healing is further compromised and normal tissues such as cartilage start to die. Osteoarthritic joints are depleted of stem cells and the healing cytokines and growth factors that are normally present in their stromal vascular fraction.
When we add stromal cells to arthritic joints we are tipping the balance of healing tissues in favor of healthy repair. Inflammation is reversed. Blood vessel walls are repaired and stop leaking. Swelling reduces and stiffness goes. When the nerves are no longer inflamed “Pain at rest” disappears. Sleep is possible again.
Tissue not cells
When we think about Osteoarthritis it is wrong to just think about cartilage cells. Many cells are involved. Many tissues are involved. Each tissue has its own SVF. This helps to explain why the results we see when using stromal cells are twice as good as those we see when using one type of cloned stem cell. The stem cell is like a general with all his underling cells and cytokines. If you send the stem cell in by itself you are sending in the general. When you use SVF you are sending in the whole army, generals included.
Progression
Mechanical factors alone do not predict progression to end stage OA.
Why do some people continue to deteriorate and suffer to the point of needing joint replacement surgery? Loss of healing ability appears to be the main factor. Cooper et al decided that while knee osteoarthritis is started by mechanical injury only those with poor healing ability went on to develop advanced OA. This changed our focus for what causes Osteoarthritis.
Early clues – related disorders
- Cardiovascular risk factors(ref)such as high cholesterol(ref) are very common in OA.
- Vascular comorbidity increases with widespread joint involvement. (ref), (ref)
- Studies have shown that cardiovascular deaths are more common with more widespread radiographic evidence of OA (ref)
- Scintigraphy has been reported to predict progression (ref) The uptake of radiolabelled bisphosphonates in joints is determined by the vascularity of the joint and the turnover of subchondral bone.It has been observed that OA progression is very unlikely in the absence of increased scintigraphic activity in the joint. This means that blood vessel deterioration possibly driven by atheromatous disease, may be a cause of progressive joint damage.
All these things suggest that blood vessels are involved in joint deterioration.
The ability to heal damage is dependant upon a good supply of all the essential nutrients, growth factors, etc and removal of waste products. Supply is a function of blood vessels. Arteries to bring it in and veins to remove the waste products and prevent build up, swelling, edema and stiffness.
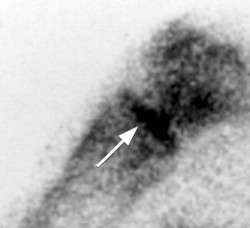
Damaged arteries reduce blood flow and supply of nutrients to tissues that are trying to heal. Damage to the veins ref)(ref) in OA is well documented. Bone marrow edema as seen on MRI represents impaired artery and vein function with bone death(,ref,ref,), swelling and edema. These MRI changes are similar to those seen in avascular necrosis(ref) and further support a primary vascular pathology for what causes Osteoarthritis.
Atheroma
Atheroma is widely known to cause heart attacks and strokes. It does this by narrowing the blood vessels which reduces blood supply slowing healing. When the artery completely blocks the tissue it is supplying then dies (Brain, Heart, Bone,etc).
In joints we see bone marrow edema on imaging. When the bone is removed for joint replacement surgery these areas can be examined under the microscope. We then see death of small pieces of bone (osteonecrosis). This is evidence of blood vessel narrowing and blockage causing tissue death the same as happens with heart attacks and strokes.
The bone under the cartilage has a very rich blood supply. When this is damaged the cartilage loses its flow of nutrients. Cartilage has no blood supply of its own. It is totally dependent on bone and synovial fluid for nutrients and waste removal.
Vascular disease is what causes Osteoarthritis to progress in most people. But it is not the only cause.
Sub-types of Osteoarthritis
Laslett et al report specific types of OA that have been proposed in the literature and may reflect how the OA was caused. This may determine how to treat each sub-type. Can we treat the cause rather than the result. Bijlsma et al proposes that if we can diagnose the cause early we can treat early to prevent progression.
- Bone-specific subtype [ref]. Patients with osteoporosis are less likely to get osteoarthritis as the severity of their osteoporosis increases. This inverse relationship sparked an interest. Increased subchondral bone loss has been observed in early osteoarthritis and in osteoporosis. This gave some support and treatment with the drugs (Bisphosphonates) used to treat osteoporosis were proposed as a treatment option. Bisphosphonates work by slowing the breakdown of bone (inhibiting osteoclasts) and they have an anti-inflammatory action. Results to support the use of bisphosphonates have been very mixed (ref). This reflects the fact that there are many causes for osteoarthritis and the drug must be given only to those for whom it will work. This patient selection is the every day work of doctors and is also know as personalized medicine. However this can only happen if the cause of osteoarthritis is correctly diagnosed.
- Predominantly bone marrow lesions in the subchondral bone [ref]. Cartilage needs bone for physical support and nutrition. This dependance is so close that it is referred to as the bone-cartilage unit. (ref) Bone marrow lesions seen on MRI have been extensively studied after being excised during total joint replacement. Histological examination under the microscope revealed microdamage in the supporting columns (trabecular bone). (ref) The progression of Bone Marrow Lesions has been shown to be a good indicator of osteoarthritis severity and eventual joint replacement. (ref) This makes it a good measure of any treatment you may choose to try.
- Post Traumatic Osteoarthritis (PTOA)
- metabolic (including systemic inflammatory), ageing, genetic and pain.
- 59% of OA patients have metabolic Syndrome. This is the largest sub-type. Metabolic syndrome consists of central adiposity, hypertension, high blood sugar and high cholesterol or high triglycerides.
- High blood pressure damages the blood vessels in the bone that supply the cartilage. This is subchondral ischemia. The cartilage is being starved and is slowly dying.
- As sugar builds up in the body it causes a low grade inflammation. This contributes to the toxic internal environment that promotes osteoarthritis.
- Excess body fat increases the production and release of adipokines. High levels of these adipokines directly affects the joints promoting osteoarthritis. This effect is not caused by an increased weight burden as it can be seen in non-weight bearing joints such as the hands.
- Roemer et al (ref) examined 1,248 MRIs. In most cases as osteophytes got larger cartilage decreased. Meaning more severe OA was associated with larger osteophytes. 1.3% of patients had very small or absent osteophytes with severe cartilage loss. This may represent a different pathology. This group are referred to as Atrophic.
- The reverse was seen in 0.2% of cases. Large osteophytes with minimal cartilage loss. These are referred to as Hypertrophic [ref])The reverse was seen in 0.2% of cases. Large osteophytes with minimal cartilage loss. These are referred to as Hypertrophic [ref])
The cause of OA by location
- Hip and knee OA can result from the majority of the subtypes,(ref)
- Thumb, shoulder, elbow and ankle OA are mainly caused by post-traumatic stresses [ref].
- Distal finger joints can be affected by a very rare OA called Erosive Osteoarthritis (EOA)
- Osteoarthritis of the hand is not related to mechanical stress like it is in the knee. Mostly osteoarthritis of the hand is caused by the systemic changes of the metabolic syndrome. (ref)
Body type for Osteoarthritis
OA patients have stronger body build and are more obese than patients with osteoporosis. They also have a higher Bone Mass Density and do not lose bone as rapidly as patients with Osteoporosis. OA patients have larger, stronger bones with fewer fragility fractures. (ref)
Osteoporotic patients are more likely to be underweight while osteoarthritic patients are more likely to be overweight. Obesity places more stress and mechanical damage on joints. The chemical signals from fat (Adipokines) are thought to be attacking your joints making OA worse even when you are asleep. (ref)
Treatment of Arthritis
Understanding what has happened helps with the treatment of Osteoarthritis. We need to treat the blood vessels to restore health to every tissue in and around the joint.
Nerves in these tissues are caught up in the inflammatory process and start to malfunction. The purpose of nerves is to warn us of danger, of damage that is happening (Nociception). When we are at rest and not using the joint we a re causing damage so these nerves should not be active. There is no new damage to warn us about. Because the nerves are inflamed they are sending pain signals that they are generating by themselves. This is pathological. (Neuropathic pain). This is what causes “pain at rest”. We need to repair these nerves as part of our treatment. This neuropathic pain can produce changes in the spinal cord and in the brain. This is called “central sensitization” and makes our pain much more severe.